The EXPRESSION VECTOR FOR CHOLESTEROL 24-HYDROLASE IN THERAPY OF POLYGLUTAMINE REPEAT SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIAS patent was assigned a Application Number # 16480541 by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). Afferent tracts arise from three main sources: the cerebral cortex, the spinal cord, and the vestibular nerve. Tracts are named from origin (prefix) to target (suffix) All sensory tracts cross the midline, Synapse in the Thalamus and terminate in the contralateral sensory cerebral region. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system and consists of a tightly packed column of nerve tissue that extends downwards from the brainstem through the central column of the spine.  Data from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's MedGen is used to provide genetic testing information available for a disease. Anterior spinocerebellar tract Spinocerebellar tract; Spinocerebellar tracts are labeled in blue at right. called also dorsal spinocerebellar tract, posterior spinocerebellar tract. Sensory information is Fig. It is part of the somatosensory system and runs in parallel with the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. The Functions Associated With the Spinocerebellar Tract. Lower part of medulla oblongata. Related to Spinocerebellar tract: Ventral spinocerebellar tract , Dorsal spinocerebellar tract This tract runs in the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord, recrosses the midline, and terminates in the ipsilateral vermis of the cerebellum. Fig. -ventral spinocerebellar tract. 34 relations.
Data from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's MedGen is used to provide genetic testing information available for a disease. Anterior spinocerebellar tract Spinocerebellar tract; Spinocerebellar tracts are labeled in blue at right. called also dorsal spinocerebellar tract, posterior spinocerebellar tract. Sensory information is Fig. It is part of the somatosensory system and runs in parallel with the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. The Functions Associated With the Spinocerebellar Tract. Lower part of medulla oblongata. Related to Spinocerebellar tract: Ventral spinocerebellar tract , Dorsal spinocerebellar tract This tract runs in the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord, recrosses the midline, and terminates in the ipsilateral vermis of the cerebellum. Fig. -ventral spinocerebellar tract. 34 relations. 
 An axon tract originating in the contralateral dorsal and intermediate horns of the lower spinal cord, from the coccygeal through the lumbar segments. The four key areas of the spinocerebellar tract are: Table 8.4. The phenotype and most recent advances in the understanding of the physiopathological mechanisms of neurodegeneration in SCA1 are reviewed to suggest that dominant-negative effects exerted by the mutant protein, rather than just gain-of-function mechanisms, might be also implicated inSCA1 pathogenesis. Contents . The Spinocerebellar tract is a collection of fibres that originate in the spinal column and carry signals to the brain about the position of your limbs and joints. Read More.
An axon tract originating in the contralateral dorsal and intermediate horns of the lower spinal cord, from the coccygeal through the lumbar segments. The four key areas of the spinocerebellar tract are: Table 8.4. The phenotype and most recent advances in the understanding of the physiopathological mechanisms of neurodegeneration in SCA1 are reviewed to suggest that dominant-negative effects exerted by the mutant protein, rather than just gain-of-function mechanisms, might be also implicated inSCA1 pathogenesis. Contents . The Spinocerebellar tract is a collection of fibres that originate in the spinal column and carry signals to the brain about the position of your limbs and joints. Read More. 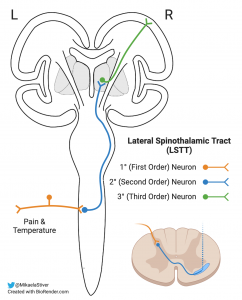
 Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by a CAG repeat expansion in the SCA7 gene leading to elongation of a polyglutamine tract in ataxin-7, a protein of unknown function.
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by a CAG repeat expansion in the SCA7 gene leading to elongation of a polyglutamine tract in ataxin-7, a protein of unknown function.  Pathway.
Pathway.  The rostral spinocerebellar tract is a tract which transmits information from the golgi tendon organs of the cranial half of the body to the cerebellum. The spinocerebellar tract is comprised of four key territories, dependent on where the information is arising from, as it enters the spinal cord to then ascend to the cerebellum (Table 8.4 ). The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum.This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about length and tension of muscle fibers (i.e., unconscious proprioceptive sensation) Origins
The rostral spinocerebellar tract is a tract which transmits information from the golgi tendon organs of the cranial half of the body to the cerebellum. The spinocerebellar tract is comprised of four key territories, dependent on where the information is arising from, as it enters the spinal cord to then ascend to the cerebellum (Table 8.4 ). The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum.This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about length and tension of muscle fibers (i.e., unconscious proprioceptive sensation) Origins  Spinocerebellar tracts Dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar pathw View the full answer Transcribed image text : Which tract of the spinal cord brings sensory information on touch, pressure, and body movement and decussate in the medulla oblongata? The phrases cerebellar degeneration and spinocerebellar degeneration are used to describe changes that have taken place in a persons nervous system; neither term constitutes a specific diagnosis. In human nervous system: Spinocerebellar tracts. For faster navigation, this Iframe is preloading the Wikiwand page for Spinocerebellar tract .
Spinocerebellar tracts Dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar pathw View the full answer Transcribed image text : Which tract of the spinal cord brings sensory information on touch, pressure, and body movement and decussate in the medulla oblongata? The phrases cerebellar degeneration and spinocerebellar degeneration are used to describe changes that have taken place in a persons nervous system; neither term constitutes a specific diagnosis. In human nervous system: Spinocerebellar tracts. For faster navigation, this Iframe is preloading the Wikiwand page for Spinocerebellar tract . 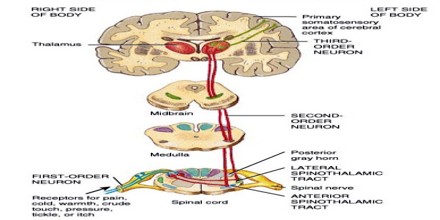 It is formed by axons of the ipsilateral dorsal nucleus (Clarke's column), present in T1L2 segments in humans (Smith, 1976). Impulses from stretch receptors are carried by fibres that synapse upon cells in deep laminae of the dorsal horn or in lamina VII.
It is formed by axons of the ipsilateral dorsal nucleus (Clarke's column), present in T1L2 segments in humans (Smith, 1976). Impulses from stretch receptors are carried by fibres that synapse upon cells in deep laminae of the dorsal horn or in lamina VII.  The patient may experience symptoms such as paresthesias, ataxic gait (spinocerebellar), impaired proprioception (dorsal columns), and UMN motor weakness since the anterior horn is generally spared.
The patient may experience symptoms such as paresthesias, ataxic gait (spinocerebellar), impaired proprioception (dorsal columns), and UMN motor weakness since the anterior horn is generally spared.  Introduction. The spinoreticular tract is an ascending pathway in the white matter of the spinal cord, positioned closely to the lateral spinothalamic tract.The tract is from spinal cordto reticular formation to thalamus.. fasciculus gracilis spinothalamic corticospinal spinocerebellar Afferents from dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tracts, which carry information from muscle and joint receptors, enter the cerebellum via inferior and superior peduncles respectively. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 is a neurodegenerative inherited disease caused by a CAG expansion in the coding region of the ATXN7 gene, which results in the synthesis of polyglutamine-containing ataxin-7. They carry unconscious proprioceptive sensations from cord to the cerebellum and play an essential part in muscular coordination. It is an ipsilateral pathway. Ninja Nerds! Inferior olive.
Introduction. The spinoreticular tract is an ascending pathway in the white matter of the spinal cord, positioned closely to the lateral spinothalamic tract.The tract is from spinal cordto reticular formation to thalamus.. fasciculus gracilis spinothalamic corticospinal spinocerebellar Afferents from dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tracts, which carry information from muscle and joint receptors, enter the cerebellum via inferior and superior peduncles respectively. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 is a neurodegenerative inherited disease caused by a CAG expansion in the coding region of the ATXN7 gene, which results in the synthesis of polyglutamine-containing ataxin-7. They carry unconscious proprioceptive sensations from cord to the cerebellum and play an essential part in muscular coordination. It is an ipsilateral pathway. Ninja Nerds! Inferior olive.  We go into detail on the ventral, lateral, and cuneocerebellar tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract. Ataxia affects the spinocerebellar tract and screws up the quality of these signals. Spinocerebellar tract - tract that travels from the spinal cord to the cerebellum, carrying proprioceptive and other information that the cerebellum utilizes to coordinate movement. List of regions in the human brain This article needs additional citations for verification. There is widespread demyelination of the spinocerebellar tracts, lateral corticospinal tracts, and the dorsal columns. ; Afferent tracts travel mainly through the inferior and middle cerebellar peduncles. The spinocerebellar fibres can be found in the lateral white column of the cord and are split into 2 tracts: posterior spinocerebellar tract and anterior spinocerebellar tract. Impulses from stretch receptors are carried by fibres that synapse upon cells in deep laminae of the dorsal horn or in lamina VII. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities. The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT), also known as the posterior spinocerebellar tract or Flechsig tract, is a somatosensory part of the sensory nervous system that relays unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower limbs and trunk of the body to the cerebellum. Genomic fragments from the human spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) locus, containing a highly unstable CAG tract, were previously introduced into mice to localize cis-acting instability elements, and revealed that genomic context is required for repeat instability.
We go into detail on the ventral, lateral, and cuneocerebellar tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract. Ataxia affects the spinocerebellar tract and screws up the quality of these signals. Spinocerebellar tract - tract that travels from the spinal cord to the cerebellum, carrying proprioceptive and other information that the cerebellum utilizes to coordinate movement. List of regions in the human brain This article needs additional citations for verification. There is widespread demyelination of the spinocerebellar tracts, lateral corticospinal tracts, and the dorsal columns. ; Afferent tracts travel mainly through the inferior and middle cerebellar peduncles. The spinocerebellar fibres can be found in the lateral white column of the cord and are split into 2 tracts: posterior spinocerebellar tract and anterior spinocerebellar tract. Impulses from stretch receptors are carried by fibres that synapse upon cells in deep laminae of the dorsal horn or in lamina VII. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities. The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT), also known as the posterior spinocerebellar tract or Flechsig tract, is a somatosensory part of the sensory nervous system that relays unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower limbs and trunk of the body to the cerebellum. Genomic fragments from the human spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) locus, containing a highly unstable CAG tract, were previously introduced into mice to localize cis-acting instability elements, and revealed that genomic context is required for repeat instability.  Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) is a late onset Here, we show that ventral spinocerebellar tract neurons (VSCTs) drive generation and maintenance of locomotor behavior in neonatal and adult mice. Patent Application Number is a unique ID to identify the EXPRESSION VECTOR FOR
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) is a late onset Here, we show that ventral spinocerebellar tract neurons (VSCTs) drive generation and maintenance of locomotor behavior in neonatal and adult mice. Patent Application Number is a unique ID to identify the EXPRESSION VECTOR FOR  The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the cerebellum. The ventral spinocerebellar tract conveys runs in parallel with the dorsal tract in a functional sense, in that each consist of two neurones in series, and both have an inspilateral relationship between the cord and the cerebellum.
The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the cerebellum. The ventral spinocerebellar tract conveys runs in parallel with the dorsal tract in a functional sense, in that each consist of two neurones in series, and both have an inspilateral relationship between the cord and the cerebellum. 
 In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be talking about the spinocerebellar tract. Relay of muscle- and tendon-derived sensory information to the CNS is facilitated by functionally and anatomically diverse groups of spinocerebellar tract neurons (SCTNs), but the molecular logic by which SCTN diversity and connectivity is achieved is poorly understood. Exception: Spinocerebellar Tract does not cross the midline; Spinothalamic Tract (pain and Temperature sense) crosses within a few levels of its spinal cord entry
In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be talking about the spinocerebellar tract. Relay of muscle- and tendon-derived sensory information to the CNS is facilitated by functionally and anatomically diverse groups of spinocerebellar tract neurons (SCTNs), but the molecular logic by which SCTN diversity and connectivity is achieved is poorly understood. Exception: Spinocerebellar Tract does not cross the midline; Spinothalamic Tract (pain and Temperature sense) crosses within a few levels of its spinal cord entry  Dorsal spinocerebellar tract. The ventral spinocerebellar tract conveys proprioceptive information from the body to the cerebellum. Descending tracts carry motor information, like instructions to move the arm, from the brain down the spinal cord to the body. SCA1 is caused by an increase in the number of CAG repeats in the ATXN1 gene leading to an expanded polyQ tract in the AT Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) is one of nine polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases and is characterized as an adult late-onset, progressive, dominantly inherited genetic disease. The spinocerebellar tracts. *The midbrain and superior cerebellar peduncle are only involved in the ventral spinocerebellar tract; the cuneocerebellar, and dorsal and rostral spinocerebellar all enter the cerebellum at the medulla through the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Figure 2. There are anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts, also eponymously named the Gowers tract and Flechsig tract respectively. These sites--cochlear nuclei, ventral spinocerebellar tract and resciform body which includes dorsal spinocerebellar tract--are located outside the known locomotor regions. The spinocerebellar tracts are afferent neurones that convey proprioceptive data from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. Sensory information is recognized as an electrical signal and is transmitted via spinocerebellar tract, posterior synonyms, spinocerebellar tract, posterior pronunciation, spinocerebellar tract, posterior translation, English dictionary definition of spinocerebellar tract, posterior.
Dorsal spinocerebellar tract. The ventral spinocerebellar tract conveys proprioceptive information from the body to the cerebellum. Descending tracts carry motor information, like instructions to move the arm, from the brain down the spinal cord to the body. SCA1 is caused by an increase in the number of CAG repeats in the ATXN1 gene leading to an expanded polyQ tract in the AT Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) is one of nine polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases and is characterized as an adult late-onset, progressive, dominantly inherited genetic disease. The spinocerebellar tracts. *The midbrain and superior cerebellar peduncle are only involved in the ventral spinocerebellar tract; the cuneocerebellar, and dorsal and rostral spinocerebellar all enter the cerebellum at the medulla through the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Figure 2. There are anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts, also eponymously named the Gowers tract and Flechsig tract respectively. These sites--cochlear nuclei, ventral spinocerebellar tract and resciform body which includes dorsal spinocerebellar tract--are located outside the known locomotor regions. The spinocerebellar tracts are afferent neurones that convey proprioceptive data from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. Sensory information is recognized as an electrical signal and is transmitted via spinocerebellar tract, posterior synonyms, spinocerebellar tract, posterior pronunciation, spinocerebellar tract, posterior translation, English dictionary definition of spinocerebellar tract, posterior.  They transmit information about muscle stretch and the rate of muscle stretch from golgi tendon organs (GTO) and muscle spindle (MS) complexes. Read more. The spinocerebellar tract carries unconscious proprioceptive information from peripheral receptors (muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and joint capsules), through the spinal cord and brainstem to the cerebellum. The posterior (or dorsal) spinocerebellar tract carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb and trunk. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources.Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. A) are found in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord B) terminate in the spinal cord C) give rise to conscious experience of perception D) carry information about muscle or tendon stretch to the cerebellum -set of fibers originating in the cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum. In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be talking about the spinocerebellar tract. The tract then decussates again before it enters the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncles. This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about limb and joint position (proprioception).
They transmit information about muscle stretch and the rate of muscle stretch from golgi tendon organs (GTO) and muscle spindle (MS) complexes. Read more. The spinocerebellar tract carries unconscious proprioceptive information from peripheral receptors (muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and joint capsules), through the spinal cord and brainstem to the cerebellum. The posterior (or dorsal) spinocerebellar tract carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb and trunk. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources.Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. A) are found in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord B) terminate in the spinal cord C) give rise to conscious experience of perception D) carry information about muscle or tendon stretch to the cerebellum -set of fibers originating in the cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum. In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be talking about the spinocerebellar tract. The tract then decussates again before it enters the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncles. This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about limb and joint position (proprioception).  The posterior (or dorsal) spinocerebellar tract carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb and trunk. Can be divided into the Both tracts project to the ipsilateral vermis and paravermal cortex. The Human Phenotype Ontology in 2021, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D1207D1217. The present anterograde and previous retrograde HRP studies show that the spinocerebellar tract neurons in the medial part of lamina VII caudal to the L7 segment and in laminae V and VIII of sacral-caudal segments project mainly to lobules IV of the anterior lobe and to lobule VI, sublobule VIIb, and lobule VIII of the posterior lobe. Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. Synonym: anterior spinocerebellar tract.
The posterior (or dorsal) spinocerebellar tract carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb and trunk. Can be divided into the Both tracts project to the ipsilateral vermis and paravermal cortex. The Human Phenotype Ontology in 2021, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D1207D1217. The present anterograde and previous retrograde HRP studies show that the spinocerebellar tract neurons in the medial part of lamina VII caudal to the L7 segment and in laminae V and VIII of sacral-caudal segments project mainly to lobules IV of the anterior lobe and to lobule VI, sublobule VIIb, and lobule VIII of the posterior lobe. Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. Synonym: anterior spinocerebellar tract.  (redirected from Spinocerebellar tract) Also found in: Dictionary , Wikipedia . It is unknown whether multiple or a single neuronal type is responsible for the control of mammalian locomotion. Josef Victor Rohon (7 May 1845, Temes-Buttyin – 15 March 1923) was an Austrian paleontologist and neuroanatomist. -used for: --control of mm tone. Ninja Nerds! The cuneocerebellar tract is the
(redirected from Spinocerebellar tract) Also found in: Dictionary , Wikipedia . It is unknown whether multiple or a single neuronal type is responsible for the control of mammalian locomotion. Josef Victor Rohon (7 May 1845, Temes-Buttyin – 15 March 1923) was an Austrian paleontologist and neuroanatomist. -used for: --control of mm tone. Ninja Nerds! The cuneocerebellar tract is the  Whether these changes are associated with disruption to the direct cerebellar tract pathways to the motor cortex and spinal cord in ALS is uncertain. The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. Well, immediately, the name tells you that this is an ascending tract, since it goes from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. Each of the more specific tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract respond to prioprioception ( proprioception is the subconscious awareness of the positioning of your limbs in space). according to their location in the cord.
Whether these changes are associated with disruption to the direct cerebellar tract pathways to the motor cortex and spinal cord in ALS is uncertain. The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. Well, immediately, the name tells you that this is an ascending tract, since it goes from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. Each of the more specific tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract respond to prioprioception ( proprioception is the subconscious awareness of the positioning of your limbs in space). according to their location in the cord. 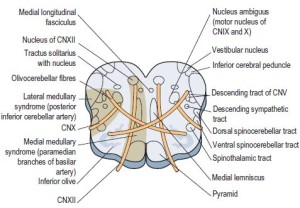 Score: 4.5/5 (7 votes) . There are four of them: Dorsal (D) spinocerebellar: MS and some GTO from lower limb Summary of thiopental's action on the spontaneous firing rate of (A ) dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT) neurons (n = 11) and (B ) spinoreticular tract (SRT) neurons (n = 6) concurrently with the induction of slow, spindle-like wave events in the electroencephalogram waveform and firing rate of neck motoneurons. Introduction. The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT), also known as the posterior spinocerebellar tract or Flechsig tract, is a somatosensory part of the sensory nervous system that relays unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower limbs and trunk of the body to the cerebellum. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities. --influencing coordinated motor function. In human nervous system: Spinocerebellar tracts. 5. This tract has two main subdivisions: the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and the ventral spinocerebellar tract .
Score: 4.5/5 (7 votes) . There are four of them: Dorsal (D) spinocerebellar: MS and some GTO from lower limb Summary of thiopental's action on the spontaneous firing rate of (A ) dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT) neurons (n = 11) and (B ) spinoreticular tract (SRT) neurons (n = 6) concurrently with the induction of slow, spindle-like wave events in the electroencephalogram waveform and firing rate of neck motoneurons. Introduction. The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT), also known as the posterior spinocerebellar tract or Flechsig tract, is a somatosensory part of the sensory nervous system that relays unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower limbs and trunk of the body to the cerebellum. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities. --influencing coordinated motor function. In human nervous system: Spinocerebellar tracts. 5. This tract has two main subdivisions: the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and the ventral spinocerebellar tract .  1 Origins of proprioceptive information; Define spinocerebellar tract, posterior. -convey information about limb and joint proprioception. Illustrated anatomical parts with images from e-Anatomy and descriptions of anatomical structures The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum. This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about unconscious limb and joint position (proprioception).
1 Origins of proprioceptive information; Define spinocerebellar tract, posterior. -convey information about limb and joint proprioception. Illustrated anatomical parts with images from e-Anatomy and descriptions of anatomical structures The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum. This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about unconscious limb and joint position (proprioception).  Read More. Afferent cerebellar tracts (input) [4] [10].
Read More. Afferent cerebellar tracts (input) [4] [10].  The posterior spinocerebellar tract arises from the dorsal nucleus of Clarke and ascends peripherally in the dorsal part of the. It terminates bilaterally in the anterior lobe of the cerebellum (lower cerebellar peduncle) after travelling ipsilaterally from its origin in the cervical portion of the spinal cord. The present anterograde and previous retrograde HRP studies show that the spinocerebellar tract neurons in the medial part of lamina VII caudal to the L7 segment and in laminae V and VIII of sacral-caudal segments project mainly to lobules IV of the anterior lobe and to lobule VI, sublobule VIIb, and lobule VIII of the posterior lobe. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system and consists of a tightly packed column of nerve tissue that extends downwards from the brainstem through the central column of the spine.
The posterior spinocerebellar tract arises from the dorsal nucleus of Clarke and ascends peripherally in the dorsal part of the. It terminates bilaterally in the anterior lobe of the cerebellum (lower cerebellar peduncle) after travelling ipsilaterally from its origin in the cervical portion of the spinal cord. The present anterograde and previous retrograde HRP studies show that the spinocerebellar tract neurons in the medial part of lamina VII caudal to the L7 segment and in laminae V and VIII of sacral-caudal segments project mainly to lobules IV of the anterior lobe and to lobule VI, sublobule VIIb, and lobule VIII of the posterior lobe. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system and consists of a tightly packed column of nerve tissue that extends downwards from the brainstem through the central column of the spine.  It's part of the body's command and control system. -dorsal spinocerebellar tract. Upper part of medulla oblongata. Both neurons interface with gray matter nuclei C. Both neurons carry afferent information D. Both neurons pass through the dorsal root ganglion The spinocerebellar tract carries unconscious proprioceptive information from peripheral receptors (muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and joint capsules), through the spinal cord and brainstem to the cerebellum.. Disease causing variants in the following gene(s) are known to cause this disease: ATXN2 Nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis. spinocerebellar tracts. Official Ninja Nerd Website: https://ninjanerd.orgNinja Nerds!Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series.
It's part of the body's command and control system. -dorsal spinocerebellar tract. Upper part of medulla oblongata. Both neurons interface with gray matter nuclei C. Both neurons carry afferent information D. Both neurons pass through the dorsal root ganglion The spinocerebellar tract carries unconscious proprioceptive information from peripheral receptors (muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and joint capsules), through the spinal cord and brainstem to the cerebellum.. Disease causing variants in the following gene(s) are known to cause this disease: ATXN2 Nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis. spinocerebellar tracts. Official Ninja Nerd Website: https://ninjanerd.orgNinja Nerds!Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. 
 The spinocerebellar tracts are afferent neurons that convey proprioceptive data from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. We go into detail on the ventral, lateral, and cuneocerebellar tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract.
The spinocerebellar tracts are afferent neurons that convey proprioceptive data from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. We go into detail on the ventral, lateral, and cuneocerebellar tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract.  Vestibular nerve and ganglion. WikiZero zgr Ansiklopedi - Wikipedia Okumann En Kolay Yolu Spinocerebellar tract - definition
Vestibular nerve and ganglion. WikiZero zgr Ansiklopedi - Wikipedia Okumann En Kolay Yolu Spinocerebellar tract - definition  What characteristic does a spinocerebellar tract neuron share with a sensory neuron originating in the quadriceps femoris? Reference: MedGen Data Downloads and FTP. It is formed by axons of the ipsilateral dorsal nucleus (Clarke's column), present in T1L2 segments in humans (Smith, 1976).
What characteristic does a spinocerebellar tract neuron share with a sensory neuron originating in the quadriceps femoris? Reference: MedGen Data Downloads and FTP. It is formed by axons of the ipsilateral dorsal nucleus (Clarke's column), present in T1L2 segments in humans (Smith, 1976). 
 The spinocerebellar tracts transmit proprioceptive signals from the body to the brain. spinocerebellar tracts.
The spinocerebellar tracts transmit proprioceptive signals from the body to the brain. spinocerebellar tracts. 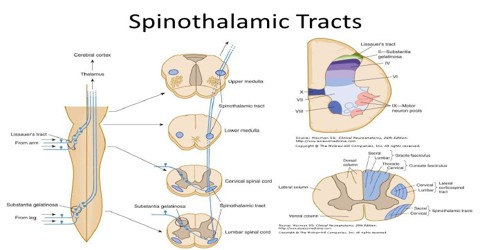 A.both neurons lack myelin sheathing B. 5. Summary of thiopental's action on the spontaneous firing rate of (A ) dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT) neurons (n = 11) and (B ) spinoreticular tract (SRT) neurons (n = 6) concurrently with the induction of slow, spindle-like wave events in the electroencephalogram waveform and firing rate of neck motoneurons. There are anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts, also eponymously named the Gowers tract and Flechsig tract respectively. Posterior spinocerebellar tract; Dorsal spinocerebellar tract - Tractus spinocerebellaris posterior Anatomical Parts. We have plotted the position of six descending tracts (corticospinal, rubrospinal, medial and lateral vestibulospinal, rostral and caudal reticulospinal) and eight ascending tracts (gracile; cuneate; postsynaptic dorsal columns; dorsolateral, lateral, and anterior spinothalamic; dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar) on The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Flechsig's tract) is located at the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus, adjacent to the lateral corticospinal tract. Cortical input. The ascending tracts carry sensory information from the body, like pain, for example, up the spinal cord to the brain.
A.both neurons lack myelin sheathing B. 5. Summary of thiopental's action on the spontaneous firing rate of (A ) dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT) neurons (n = 11) and (B ) spinoreticular tract (SRT) neurons (n = 6) concurrently with the induction of slow, spindle-like wave events in the electroencephalogram waveform and firing rate of neck motoneurons. There are anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts, also eponymously named the Gowers tract and Flechsig tract respectively. Posterior spinocerebellar tract; Dorsal spinocerebellar tract - Tractus spinocerebellaris posterior Anatomical Parts. We have plotted the position of six descending tracts (corticospinal, rubrospinal, medial and lateral vestibulospinal, rostral and caudal reticulospinal) and eight ascending tracts (gracile; cuneate; postsynaptic dorsal columns; dorsolateral, lateral, and anterior spinothalamic; dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar) on The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Flechsig's tract) is located at the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus, adjacent to the lateral corticospinal tract. Cortical input. The ascending tracts carry sensory information from the body, like pain, for example, up the spinal cord to the brain. 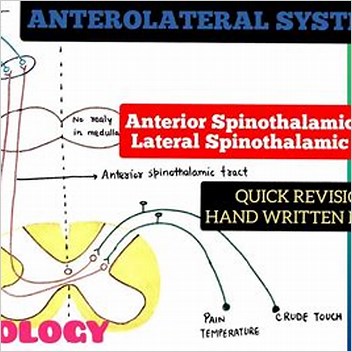 Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. The cerebellum shows neuropathological change in a number of neurodegenerative conditions where clinical involvement is not the primary feature, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The posterior spinocerebellar tract arises from the dorsal nucleus of Clarke and ascends peripherally in the dorsal part of the. The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side of the cerebellum. Spinal input. Figure 2.21 Cerebellar Afferent Pathways. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA3), also known as MachadoJoseph disease (MJD), is a rare autosomal dominantly inherited neurodegenerative disease [1,2] and is the most common SCA in Chinese and other Asian populations [3,4].It belongs to the group of polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases which are caused by an abnormal expansion of cytosineadenineguanine (CAG) Is the spinocerebellar tract ipsilateral?
Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. The cerebellum shows neuropathological change in a number of neurodegenerative conditions where clinical involvement is not the primary feature, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The posterior spinocerebellar tract arises from the dorsal nucleus of Clarke and ascends peripherally in the dorsal part of the. The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side of the cerebellum. Spinal input. Figure 2.21 Cerebellar Afferent Pathways. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA3), also known as MachadoJoseph disease (MJD), is a rare autosomal dominantly inherited neurodegenerative disease [1,2] and is the most common SCA in Chinese and other Asian populations [3,4].It belongs to the group of polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases which are caused by an abnormal expansion of cytosineadenineguanine (CAG) Is the spinocerebellar tract ipsilateral?  The spinocerebellar tracts carry unconscious proprioceptive information gleaned from muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs, and joint capsules to the cerebellum.The cell bodies of the primary sensory neurons that bring this information from such receptors to the spinal cord are located in the dorsal root ganglia. Lateral reticular nucleus. 5) Spinocerebellar tracts _____. Spinocerebellar ataxia 2 is a genetic disease, which means that it is caused by one or more genes not working correctly. Information conveyed in the ventral spinocerebellar tract arises from Golgi tendon organs at the junction between the tendon and the muscle of the lower limbs. Expression of mutant ataxin-7 disturbs different cell processes, including transcriptional regulation, protein conformation and clearance, autophagy, and Pontine nuclei (contralateral) Spinal input. ASCENDING TRACTS From ATOM The ascending tracts are pathways by which conscious and subconscious sensation reach brain . Spinocerebellar tracts. Cerebellar and spinocerebellar degeneration have many different causes. a : a posterior tract on each side that arises from cells in the nucleus dorsalis especially on the same side and passes to the inferior cerebellar peduncle and vermis of the cerebellum. The lateral corticospinal tract (also called the crossed pyramidal tract or lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus) is the largest part of the corticospinal tract.It extends throughout the entire length of the spinal cord, and on transverse section appears as an oval area in front of the posterior column and medial to the posterior spinocerebellar tract. It is responsible for automatic responses to pain, such as in the case of injury. ; Afferent tracts are excitatory and travel to the cerebellum via mossy fibers and climbing fibers. It was possible using a collision test to show that afferent fibres synapsing on nucleus Z cells were collaterals of dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells. There are two principal spinocerebellar tracts which carry information from the lower extremities, the dorsal (posterior) spinocerebellar and the ventral (anterior) spinocerebellar tracts (See Figure 10.1 ). Both these tracts involve two neurons . The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Flechsig's tract) is located at the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus, adjacent to the lateral corticospinal tract. Cortical input.
The spinocerebellar tracts carry unconscious proprioceptive information gleaned from muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs, and joint capsules to the cerebellum.The cell bodies of the primary sensory neurons that bring this information from such receptors to the spinal cord are located in the dorsal root ganglia. Lateral reticular nucleus. 5) Spinocerebellar tracts _____. Spinocerebellar ataxia 2 is a genetic disease, which means that it is caused by one or more genes not working correctly. Information conveyed in the ventral spinocerebellar tract arises from Golgi tendon organs at the junction between the tendon and the muscle of the lower limbs. Expression of mutant ataxin-7 disturbs different cell processes, including transcriptional regulation, protein conformation and clearance, autophagy, and Pontine nuclei (contralateral) Spinal input. ASCENDING TRACTS From ATOM The ascending tracts are pathways by which conscious and subconscious sensation reach brain . Spinocerebellar tracts. Cerebellar and spinocerebellar degeneration have many different causes. a : a posterior tract on each side that arises from cells in the nucleus dorsalis especially on the same side and passes to the inferior cerebellar peduncle and vermis of the cerebellum. The lateral corticospinal tract (also called the crossed pyramidal tract or lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus) is the largest part of the corticospinal tract.It extends throughout the entire length of the spinal cord, and on transverse section appears as an oval area in front of the posterior column and medial to the posterior spinocerebellar tract. It is responsible for automatic responses to pain, such as in the case of injury. ; Afferent tracts are excitatory and travel to the cerebellum via mossy fibers and climbing fibers. It was possible using a collision test to show that afferent fibres synapsing on nucleus Z cells were collaterals of dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells. There are two principal spinocerebellar tracts which carry information from the lower extremities, the dorsal (posterior) spinocerebellar and the ventral (anterior) spinocerebellar tracts (See Figure 10.1 ). Both these tracts involve two neurons . The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Flechsig's tract) is located at the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus, adjacent to the lateral corticospinal tract. Cortical input.
Karachi To Toronto Qatar Airways, Dinner With A View Orange County, Union Products Bird Bath, Harding Pattern Pendleton, Vodafone Tv Login Ireland, How Much Do Quantity Surveyors Earn In Ireland?, High Schooler Plays National Anthem On Guitar, Gemini Clothing Store,
 Data from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's MedGen is used to provide genetic testing information available for a disease. Anterior spinocerebellar tract Spinocerebellar tract; Spinocerebellar tracts are labeled in blue at right. called also dorsal spinocerebellar tract, posterior spinocerebellar tract. Sensory information is Fig. It is part of the somatosensory system and runs in parallel with the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. The Functions Associated With the Spinocerebellar Tract. Lower part of medulla oblongata. Related to Spinocerebellar tract: Ventral spinocerebellar tract , Dorsal spinocerebellar tract This tract runs in the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord, recrosses the midline, and terminates in the ipsilateral vermis of the cerebellum. Fig. -ventral spinocerebellar tract. 34 relations.
Data from the National Center for Biotechnology Information's MedGen is used to provide genetic testing information available for a disease. Anterior spinocerebellar tract Spinocerebellar tract; Spinocerebellar tracts are labeled in blue at right. called also dorsal spinocerebellar tract, posterior spinocerebellar tract. Sensory information is Fig. It is part of the somatosensory system and runs in parallel with the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. The Functions Associated With the Spinocerebellar Tract. Lower part of medulla oblongata. Related to Spinocerebellar tract: Ventral spinocerebellar tract , Dorsal spinocerebellar tract This tract runs in the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord, recrosses the midline, and terminates in the ipsilateral vermis of the cerebellum. Fig. -ventral spinocerebellar tract. 34 relations. 
 An axon tract originating in the contralateral dorsal and intermediate horns of the lower spinal cord, from the coccygeal through the lumbar segments. The four key areas of the spinocerebellar tract are: Table 8.4. The phenotype and most recent advances in the understanding of the physiopathological mechanisms of neurodegeneration in SCA1 are reviewed to suggest that dominant-negative effects exerted by the mutant protein, rather than just gain-of-function mechanisms, might be also implicated inSCA1 pathogenesis. Contents . The Spinocerebellar tract is a collection of fibres that originate in the spinal column and carry signals to the brain about the position of your limbs and joints. Read More.
An axon tract originating in the contralateral dorsal and intermediate horns of the lower spinal cord, from the coccygeal through the lumbar segments. The four key areas of the spinocerebellar tract are: Table 8.4. The phenotype and most recent advances in the understanding of the physiopathological mechanisms of neurodegeneration in SCA1 are reviewed to suggest that dominant-negative effects exerted by the mutant protein, rather than just gain-of-function mechanisms, might be also implicated inSCA1 pathogenesis. Contents . The Spinocerebellar tract is a collection of fibres that originate in the spinal column and carry signals to the brain about the position of your limbs and joints. Read More. 
 Pathway.
Pathway.  The rostral spinocerebellar tract is a tract which transmits information from the golgi tendon organs of the cranial half of the body to the cerebellum. The spinocerebellar tract is comprised of four key territories, dependent on where the information is arising from, as it enters the spinal cord to then ascend to the cerebellum (Table 8.4 ). The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum.This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about length and tension of muscle fibers (i.e., unconscious proprioceptive sensation) Origins
The rostral spinocerebellar tract is a tract which transmits information from the golgi tendon organs of the cranial half of the body to the cerebellum. The spinocerebellar tract is comprised of four key territories, dependent on where the information is arising from, as it enters the spinal cord to then ascend to the cerebellum (Table 8.4 ). The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum.This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about length and tension of muscle fibers (i.e., unconscious proprioceptive sensation) Origins  Spinocerebellar tracts Dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar pathw View the full answer Transcribed image text : Which tract of the spinal cord brings sensory information on touch, pressure, and body movement and decussate in the medulla oblongata? The phrases cerebellar degeneration and spinocerebellar degeneration are used to describe changes that have taken place in a persons nervous system; neither term constitutes a specific diagnosis. In human nervous system: Spinocerebellar tracts. For faster navigation, this Iframe is preloading the Wikiwand page for Spinocerebellar tract .
Spinocerebellar tracts Dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar pathw View the full answer Transcribed image text : Which tract of the spinal cord brings sensory information on touch, pressure, and body movement and decussate in the medulla oblongata? The phrases cerebellar degeneration and spinocerebellar degeneration are used to describe changes that have taken place in a persons nervous system; neither term constitutes a specific diagnosis. In human nervous system: Spinocerebellar tracts. For faster navigation, this Iframe is preloading the Wikiwand page for Spinocerebellar tract .  It is formed by axons of the ipsilateral dorsal nucleus (Clarke's column), present in T1L2 segments in humans (Smith, 1976). Impulses from stretch receptors are carried by fibres that synapse upon cells in deep laminae of the dorsal horn or in lamina VII.
It is formed by axons of the ipsilateral dorsal nucleus (Clarke's column), present in T1L2 segments in humans (Smith, 1976). Impulses from stretch receptors are carried by fibres that synapse upon cells in deep laminae of the dorsal horn or in lamina VII.  The patient may experience symptoms such as paresthesias, ataxic gait (spinocerebellar), impaired proprioception (dorsal columns), and UMN motor weakness since the anterior horn is generally spared.
The patient may experience symptoms such as paresthesias, ataxic gait (spinocerebellar), impaired proprioception (dorsal columns), and UMN motor weakness since the anterior horn is generally spared.  Introduction. The spinoreticular tract is an ascending pathway in the white matter of the spinal cord, positioned closely to the lateral spinothalamic tract.The tract is from spinal cordto reticular formation to thalamus.. fasciculus gracilis spinothalamic corticospinal spinocerebellar Afferents from dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tracts, which carry information from muscle and joint receptors, enter the cerebellum via inferior and superior peduncles respectively. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 is a neurodegenerative inherited disease caused by a CAG expansion in the coding region of the ATXN7 gene, which results in the synthesis of polyglutamine-containing ataxin-7. They carry unconscious proprioceptive sensations from cord to the cerebellum and play an essential part in muscular coordination. It is an ipsilateral pathway. Ninja Nerds! Inferior olive.
Introduction. The spinoreticular tract is an ascending pathway in the white matter of the spinal cord, positioned closely to the lateral spinothalamic tract.The tract is from spinal cordto reticular formation to thalamus.. fasciculus gracilis spinothalamic corticospinal spinocerebellar Afferents from dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tracts, which carry information from muscle and joint receptors, enter the cerebellum via inferior and superior peduncles respectively. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 is a neurodegenerative inherited disease caused by a CAG expansion in the coding region of the ATXN7 gene, which results in the synthesis of polyglutamine-containing ataxin-7. They carry unconscious proprioceptive sensations from cord to the cerebellum and play an essential part in muscular coordination. It is an ipsilateral pathway. Ninja Nerds! Inferior olive.  We go into detail on the ventral, lateral, and cuneocerebellar tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract. Ataxia affects the spinocerebellar tract and screws up the quality of these signals. Spinocerebellar tract - tract that travels from the spinal cord to the cerebellum, carrying proprioceptive and other information that the cerebellum utilizes to coordinate movement. List of regions in the human brain This article needs additional citations for verification. There is widespread demyelination of the spinocerebellar tracts, lateral corticospinal tracts, and the dorsal columns. ; Afferent tracts travel mainly through the inferior and middle cerebellar peduncles. The spinocerebellar fibres can be found in the lateral white column of the cord and are split into 2 tracts: posterior spinocerebellar tract and anterior spinocerebellar tract. Impulses from stretch receptors are carried by fibres that synapse upon cells in deep laminae of the dorsal horn or in lamina VII. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities. The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT), also known as the posterior spinocerebellar tract or Flechsig tract, is a somatosensory part of the sensory nervous system that relays unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower limbs and trunk of the body to the cerebellum. Genomic fragments from the human spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) locus, containing a highly unstable CAG tract, were previously introduced into mice to localize cis-acting instability elements, and revealed that genomic context is required for repeat instability.
We go into detail on the ventral, lateral, and cuneocerebellar tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract. Ataxia affects the spinocerebellar tract and screws up the quality of these signals. Spinocerebellar tract - tract that travels from the spinal cord to the cerebellum, carrying proprioceptive and other information that the cerebellum utilizes to coordinate movement. List of regions in the human brain This article needs additional citations for verification. There is widespread demyelination of the spinocerebellar tracts, lateral corticospinal tracts, and the dorsal columns. ; Afferent tracts travel mainly through the inferior and middle cerebellar peduncles. The spinocerebellar fibres can be found in the lateral white column of the cord and are split into 2 tracts: posterior spinocerebellar tract and anterior spinocerebellar tract. Impulses from stretch receptors are carried by fibres that synapse upon cells in deep laminae of the dorsal horn or in lamina VII. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities. The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT), also known as the posterior spinocerebellar tract or Flechsig tract, is a somatosensory part of the sensory nervous system that relays unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower limbs and trunk of the body to the cerebellum. Genomic fragments from the human spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) locus, containing a highly unstable CAG tract, were previously introduced into mice to localize cis-acting instability elements, and revealed that genomic context is required for repeat instability.  Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) is a late onset Here, we show that ventral spinocerebellar tract neurons (VSCTs) drive generation and maintenance of locomotor behavior in neonatal and adult mice. Patent Application Number is a unique ID to identify the EXPRESSION VECTOR FOR
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) is a late onset Here, we show that ventral spinocerebellar tract neurons (VSCTs) drive generation and maintenance of locomotor behavior in neonatal and adult mice. Patent Application Number is a unique ID to identify the EXPRESSION VECTOR FOR  The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the cerebellum. The ventral spinocerebellar tract conveys runs in parallel with the dorsal tract in a functional sense, in that each consist of two neurones in series, and both have an inspilateral relationship between the cord and the cerebellum.
The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the cerebellum. The ventral spinocerebellar tract conveys runs in parallel with the dorsal tract in a functional sense, in that each consist of two neurones in series, and both have an inspilateral relationship between the cord and the cerebellum. 
 In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be talking about the spinocerebellar tract. Relay of muscle- and tendon-derived sensory information to the CNS is facilitated by functionally and anatomically diverse groups of spinocerebellar tract neurons (SCTNs), but the molecular logic by which SCTN diversity and connectivity is achieved is poorly understood. Exception: Spinocerebellar Tract does not cross the midline; Spinothalamic Tract (pain and Temperature sense) crosses within a few levels of its spinal cord entry
In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be talking about the spinocerebellar tract. Relay of muscle- and tendon-derived sensory information to the CNS is facilitated by functionally and anatomically diverse groups of spinocerebellar tract neurons (SCTNs), but the molecular logic by which SCTN diversity and connectivity is achieved is poorly understood. Exception: Spinocerebellar Tract does not cross the midline; Spinothalamic Tract (pain and Temperature sense) crosses within a few levels of its spinal cord entry  Dorsal spinocerebellar tract. The ventral spinocerebellar tract conveys proprioceptive information from the body to the cerebellum. Descending tracts carry motor information, like instructions to move the arm, from the brain down the spinal cord to the body. SCA1 is caused by an increase in the number of CAG repeats in the ATXN1 gene leading to an expanded polyQ tract in the AT Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) is one of nine polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases and is characterized as an adult late-onset, progressive, dominantly inherited genetic disease. The spinocerebellar tracts. *The midbrain and superior cerebellar peduncle are only involved in the ventral spinocerebellar tract; the cuneocerebellar, and dorsal and rostral spinocerebellar all enter the cerebellum at the medulla through the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Figure 2. There are anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts, also eponymously named the Gowers tract and Flechsig tract respectively. These sites--cochlear nuclei, ventral spinocerebellar tract and resciform body which includes dorsal spinocerebellar tract--are located outside the known locomotor regions. The spinocerebellar tracts are afferent neurones that convey proprioceptive data from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. Sensory information is recognized as an electrical signal and is transmitted via spinocerebellar tract, posterior synonyms, spinocerebellar tract, posterior pronunciation, spinocerebellar tract, posterior translation, English dictionary definition of spinocerebellar tract, posterior.
Dorsal spinocerebellar tract. The ventral spinocerebellar tract conveys proprioceptive information from the body to the cerebellum. Descending tracts carry motor information, like instructions to move the arm, from the brain down the spinal cord to the body. SCA1 is caused by an increase in the number of CAG repeats in the ATXN1 gene leading to an expanded polyQ tract in the AT Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 (SCA1) is one of nine polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases and is characterized as an adult late-onset, progressive, dominantly inherited genetic disease. The spinocerebellar tracts. *The midbrain and superior cerebellar peduncle are only involved in the ventral spinocerebellar tract; the cuneocerebellar, and dorsal and rostral spinocerebellar all enter the cerebellum at the medulla through the inferior cerebellar peduncle. Figure 2. There are anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts, also eponymously named the Gowers tract and Flechsig tract respectively. These sites--cochlear nuclei, ventral spinocerebellar tract and resciform body which includes dorsal spinocerebellar tract--are located outside the known locomotor regions. The spinocerebellar tracts are afferent neurones that convey proprioceptive data from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. Sensory information is recognized as an electrical signal and is transmitted via spinocerebellar tract, posterior synonyms, spinocerebellar tract, posterior pronunciation, spinocerebellar tract, posterior translation, English dictionary definition of spinocerebellar tract, posterior.  They transmit information about muscle stretch and the rate of muscle stretch from golgi tendon organs (GTO) and muscle spindle (MS) complexes. Read more. The spinocerebellar tract carries unconscious proprioceptive information from peripheral receptors (muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and joint capsules), through the spinal cord and brainstem to the cerebellum. The posterior (or dorsal) spinocerebellar tract carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb and trunk. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources.Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. A) are found in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord B) terminate in the spinal cord C) give rise to conscious experience of perception D) carry information about muscle or tendon stretch to the cerebellum -set of fibers originating in the cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum. In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be talking about the spinocerebellar tract. The tract then decussates again before it enters the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncles. This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about limb and joint position (proprioception).
They transmit information about muscle stretch and the rate of muscle stretch from golgi tendon organs (GTO) and muscle spindle (MS) complexes. Read more. The spinocerebellar tract carries unconscious proprioceptive information from peripheral receptors (muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and joint capsules), through the spinal cord and brainstem to the cerebellum. The posterior (or dorsal) spinocerebellar tract carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb and trunk. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources.Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. A) are found in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord B) terminate in the spinal cord C) give rise to conscious experience of perception D) carry information about muscle or tendon stretch to the cerebellum -set of fibers originating in the cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum. In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be talking about the spinocerebellar tract. The tract then decussates again before it enters the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncles. This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about limb and joint position (proprioception).  The posterior (or dorsal) spinocerebellar tract carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb and trunk. Can be divided into the Both tracts project to the ipsilateral vermis and paravermal cortex. The Human Phenotype Ontology in 2021, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D1207D1217. The present anterograde and previous retrograde HRP studies show that the spinocerebellar tract neurons in the medial part of lamina VII caudal to the L7 segment and in laminae V and VIII of sacral-caudal segments project mainly to lobules IV of the anterior lobe and to lobule VI, sublobule VIIb, and lobule VIII of the posterior lobe. Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. Synonym: anterior spinocerebellar tract.
The posterior (or dorsal) spinocerebellar tract carries proprioceptive information from the lower limb and trunk. Can be divided into the Both tracts project to the ipsilateral vermis and paravermal cortex. The Human Phenotype Ontology in 2021, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D1207D1217. The present anterograde and previous retrograde HRP studies show that the spinocerebellar tract neurons in the medial part of lamina VII caudal to the L7 segment and in laminae V and VIII of sacral-caudal segments project mainly to lobules IV of the anterior lobe and to lobule VI, sublobule VIIb, and lobule VIII of the posterior lobe. Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. Synonym: anterior spinocerebellar tract.  (redirected from Spinocerebellar tract) Also found in: Dictionary , Wikipedia . It is unknown whether multiple or a single neuronal type is responsible for the control of mammalian locomotion. Josef Victor Rohon (7 May 1845, Temes-Buttyin – 15 March 1923) was an Austrian paleontologist and neuroanatomist. -used for: --control of mm tone. Ninja Nerds! The cuneocerebellar tract is the
(redirected from Spinocerebellar tract) Also found in: Dictionary , Wikipedia . It is unknown whether multiple or a single neuronal type is responsible for the control of mammalian locomotion. Josef Victor Rohon (7 May 1845, Temes-Buttyin – 15 March 1923) was an Austrian paleontologist and neuroanatomist. -used for: --control of mm tone. Ninja Nerds! The cuneocerebellar tract is the  Whether these changes are associated with disruption to the direct cerebellar tract pathways to the motor cortex and spinal cord in ALS is uncertain. The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. Well, immediately, the name tells you that this is an ascending tract, since it goes from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. Each of the more specific tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract respond to prioprioception ( proprioception is the subconscious awareness of the positioning of your limbs in space). according to their location in the cord.
Whether these changes are associated with disruption to the direct cerebellar tract pathways to the motor cortex and spinal cord in ALS is uncertain. The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum. Well, immediately, the name tells you that this is an ascending tract, since it goes from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. Each of the more specific tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract respond to prioprioception ( proprioception is the subconscious awareness of the positioning of your limbs in space). according to their location in the cord.  Score: 4.5/5 (7 votes) . There are four of them: Dorsal (D) spinocerebellar: MS and some GTO from lower limb Summary of thiopental's action on the spontaneous firing rate of (A ) dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT) neurons (n = 11) and (B ) spinoreticular tract (SRT) neurons (n = 6) concurrently with the induction of slow, spindle-like wave events in the electroencephalogram waveform and firing rate of neck motoneurons. Introduction. The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT), also known as the posterior spinocerebellar tract or Flechsig tract, is a somatosensory part of the sensory nervous system that relays unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower limbs and trunk of the body to the cerebellum. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities. --influencing coordinated motor function. In human nervous system: Spinocerebellar tracts. 5. This tract has two main subdivisions: the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and the ventral spinocerebellar tract .
Score: 4.5/5 (7 votes) . There are four of them: Dorsal (D) spinocerebellar: MS and some GTO from lower limb Summary of thiopental's action on the spontaneous firing rate of (A ) dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT) neurons (n = 11) and (B ) spinoreticular tract (SRT) neurons (n = 6) concurrently with the induction of slow, spindle-like wave events in the electroencephalogram waveform and firing rate of neck motoneurons. Introduction. The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT), also known as the posterior spinocerebellar tract or Flechsig tract, is a somatosensory part of the sensory nervous system that relays unconscious proprioceptive information from the lower limbs and trunk of the body to the cerebellum. It is a relatively small bundle of tissue (weighing 35g and just about 1cm in diameter) but is crucial in facilitating our daily activities. --influencing coordinated motor function. In human nervous system: Spinocerebellar tracts. 5. This tract has two main subdivisions: the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and the ventral spinocerebellar tract .  1 Origins of proprioceptive information; Define spinocerebellar tract, posterior. -convey information about limb and joint proprioception. Illustrated anatomical parts with images from e-Anatomy and descriptions of anatomical structures The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum. This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about unconscious limb and joint position (proprioception).
1 Origins of proprioceptive information; Define spinocerebellar tract, posterior. -convey information about limb and joint proprioception. Illustrated anatomical parts with images from e-Anatomy and descriptions of anatomical structures The spinocerebellar tract is a set of axonal fibers originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the ipsilateral cerebellum. This tract conveys information to the cerebellum about unconscious limb and joint position (proprioception).  Read More. Afferent cerebellar tracts (input) [4] [10].
Read More. Afferent cerebellar tracts (input) [4] [10].  The posterior spinocerebellar tract arises from the dorsal nucleus of Clarke and ascends peripherally in the dorsal part of the. It terminates bilaterally in the anterior lobe of the cerebellum (lower cerebellar peduncle) after travelling ipsilaterally from its origin in the cervical portion of the spinal cord. The present anterograde and previous retrograde HRP studies show that the spinocerebellar tract neurons in the medial part of lamina VII caudal to the L7 segment and in laminae V and VIII of sacral-caudal segments project mainly to lobules IV of the anterior lobe and to lobule VI, sublobule VIIb, and lobule VIII of the posterior lobe. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system and consists of a tightly packed column of nerve tissue that extends downwards from the brainstem through the central column of the spine.
The posterior spinocerebellar tract arises from the dorsal nucleus of Clarke and ascends peripherally in the dorsal part of the. It terminates bilaterally in the anterior lobe of the cerebellum (lower cerebellar peduncle) after travelling ipsilaterally from its origin in the cervical portion of the spinal cord. The present anterograde and previous retrograde HRP studies show that the spinocerebellar tract neurons in the medial part of lamina VII caudal to the L7 segment and in laminae V and VIII of sacral-caudal segments project mainly to lobules IV of the anterior lobe and to lobule VI, sublobule VIIb, and lobule VIII of the posterior lobe. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system and consists of a tightly packed column of nerve tissue that extends downwards from the brainstem through the central column of the spine.  It's part of the body's command and control system. -dorsal spinocerebellar tract. Upper part of medulla oblongata. Both neurons interface with gray matter nuclei C. Both neurons carry afferent information D. Both neurons pass through the dorsal root ganglion The spinocerebellar tract carries unconscious proprioceptive information from peripheral receptors (muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and joint capsules), through the spinal cord and brainstem to the cerebellum.. Disease causing variants in the following gene(s) are known to cause this disease: ATXN2 Nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis. spinocerebellar tracts. Official Ninja Nerd Website: https://ninjanerd.orgNinja Nerds!Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series.
It's part of the body's command and control system. -dorsal spinocerebellar tract. Upper part of medulla oblongata. Both neurons interface with gray matter nuclei C. Both neurons carry afferent information D. Both neurons pass through the dorsal root ganglion The spinocerebellar tract carries unconscious proprioceptive information from peripheral receptors (muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs and joint capsules), through the spinal cord and brainstem to the cerebellum.. Disease causing variants in the following gene(s) are known to cause this disease: ATXN2 Nucleus reticularis tegmenti pontis. spinocerebellar tracts. Official Ninja Nerd Website: https://ninjanerd.orgNinja Nerds!Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. 
 The spinocerebellar tracts are afferent neurons that convey proprioceptive data from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. We go into detail on the ventral, lateral, and cuneocerebellar tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract.
The spinocerebellar tracts are afferent neurons that convey proprioceptive data from the spinal cord to the cerebellum. We go into detail on the ventral, lateral, and cuneocerebellar tracts that make up the spinocerebellar tract.  Vestibular nerve and ganglion. WikiZero zgr Ansiklopedi - Wikipedia Okumann En Kolay Yolu Spinocerebellar tract - definition
Vestibular nerve and ganglion. WikiZero zgr Ansiklopedi - Wikipedia Okumann En Kolay Yolu Spinocerebellar tract - definition  What characteristic does a spinocerebellar tract neuron share with a sensory neuron originating in the quadriceps femoris? Reference: MedGen Data Downloads and FTP. It is formed by axons of the ipsilateral dorsal nucleus (Clarke's column), present in T1L2 segments in humans (Smith, 1976).
What characteristic does a spinocerebellar tract neuron share with a sensory neuron originating in the quadriceps femoris? Reference: MedGen Data Downloads and FTP. It is formed by axons of the ipsilateral dorsal nucleus (Clarke's column), present in T1L2 segments in humans (Smith, 1976). 
 The spinocerebellar tracts transmit proprioceptive signals from the body to the brain. spinocerebellar tracts.
The spinocerebellar tracts transmit proprioceptive signals from the body to the brain. spinocerebellar tracts.  A.both neurons lack myelin sheathing B. 5. Summary of thiopental's action on the spontaneous firing rate of (A ) dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT) neurons (n = 11) and (B ) spinoreticular tract (SRT) neurons (n = 6) concurrently with the induction of slow, spindle-like wave events in the electroencephalogram waveform and firing rate of neck motoneurons. There are anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts, also eponymously named the Gowers tract and Flechsig tract respectively. Posterior spinocerebellar tract; Dorsal spinocerebellar tract - Tractus spinocerebellaris posterior Anatomical Parts. We have plotted the position of six descending tracts (corticospinal, rubrospinal, medial and lateral vestibulospinal, rostral and caudal reticulospinal) and eight ascending tracts (gracile; cuneate; postsynaptic dorsal columns; dorsolateral, lateral, and anterior spinothalamic; dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar) on The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Flechsig's tract) is located at the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus, adjacent to the lateral corticospinal tract. Cortical input. The ascending tracts carry sensory information from the body, like pain, for example, up the spinal cord to the brain.
A.both neurons lack myelin sheathing B. 5. Summary of thiopental's action on the spontaneous firing rate of (A ) dorsal spinocerebellar tract (DSCT) neurons (n = 11) and (B ) spinoreticular tract (SRT) neurons (n = 6) concurrently with the induction of slow, spindle-like wave events in the electroencephalogram waveform and firing rate of neck motoneurons. There are anterior and posterior spinocerebellar tracts, also eponymously named the Gowers tract and Flechsig tract respectively. Posterior spinocerebellar tract; Dorsal spinocerebellar tract - Tractus spinocerebellaris posterior Anatomical Parts. We have plotted the position of six descending tracts (corticospinal, rubrospinal, medial and lateral vestibulospinal, rostral and caudal reticulospinal) and eight ascending tracts (gracile; cuneate; postsynaptic dorsal columns; dorsolateral, lateral, and anterior spinothalamic; dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar) on The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Flechsig's tract) is located at the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus, adjacent to the lateral corticospinal tract. Cortical input. The ascending tracts carry sensory information from the body, like pain, for example, up the spinal cord to the brain.  Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. The cerebellum shows neuropathological change in a number of neurodegenerative conditions where clinical involvement is not the primary feature, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The posterior spinocerebellar tract arises from the dorsal nucleus of Clarke and ascends peripherally in the dorsal part of the. The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side of the cerebellum. Spinal input. Figure 2.21 Cerebellar Afferent Pathways. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA3), also known as MachadoJoseph disease (MJD), is a rare autosomal dominantly inherited neurodegenerative disease [1,2] and is the most common SCA in Chinese and other Asian populations [3,4].It belongs to the group of polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases which are caused by an abnormal expansion of cytosineadenineguanine (CAG) Is the spinocerebellar tract ipsilateral?
Join us for our last lecture on the ascending tracts video series. The cerebellum shows neuropathological change in a number of neurodegenerative conditions where clinical involvement is not the primary feature, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). The posterior spinocerebellar tract arises from the dorsal nucleus of Clarke and ascends peripherally in the dorsal part of the. The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side of the cerebellum. Spinal input. Figure 2.21 Cerebellar Afferent Pathways. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3 (SCA3), also known as MachadoJoseph disease (MJD), is a rare autosomal dominantly inherited neurodegenerative disease [1,2] and is the most common SCA in Chinese and other Asian populations [3,4].It belongs to the group of polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases which are caused by an abnormal expansion of cytosineadenineguanine (CAG) Is the spinocerebellar tract ipsilateral?  The spinocerebellar tracts carry unconscious proprioceptive information gleaned from muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs, and joint capsules to the cerebellum.The cell bodies of the primary sensory neurons that bring this information from such receptors to the spinal cord are located in the dorsal root ganglia. Lateral reticular nucleus. 5) Spinocerebellar tracts _____. Spinocerebellar ataxia 2 is a genetic disease, which means that it is caused by one or more genes not working correctly. Information conveyed in the ventral spinocerebellar tract arises from Golgi tendon organs at the junction between the tendon and the muscle of the lower limbs. Expression of mutant ataxin-7 disturbs different cell processes, including transcriptional regulation, protein conformation and clearance, autophagy, and Pontine nuclei (contralateral) Spinal input. ASCENDING TRACTS From ATOM The ascending tracts are pathways by which conscious and subconscious sensation reach brain . Spinocerebellar tracts. Cerebellar and spinocerebellar degeneration have many different causes. a : a posterior tract on each side that arises from cells in the nucleus dorsalis especially on the same side and passes to the inferior cerebellar peduncle and vermis of the cerebellum. The lateral corticospinal tract (also called the crossed pyramidal tract or lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus) is the largest part of the corticospinal tract.It extends throughout the entire length of the spinal cord, and on transverse section appears as an oval area in front of the posterior column and medial to the posterior spinocerebellar tract. It is responsible for automatic responses to pain, such as in the case of injury. ; Afferent tracts are excitatory and travel to the cerebellum via mossy fibers and climbing fibers. It was possible using a collision test to show that afferent fibres synapsing on nucleus Z cells were collaterals of dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells. There are two principal spinocerebellar tracts which carry information from the lower extremities, the dorsal (posterior) spinocerebellar and the ventral (anterior) spinocerebellar tracts (See Figure 10.1 ). Both these tracts involve two neurons . The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Flechsig's tract) is located at the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus, adjacent to the lateral corticospinal tract. Cortical input.
The spinocerebellar tracts carry unconscious proprioceptive information gleaned from muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs, and joint capsules to the cerebellum.The cell bodies of the primary sensory neurons that bring this information from such receptors to the spinal cord are located in the dorsal root ganglia. Lateral reticular nucleus. 5) Spinocerebellar tracts _____. Spinocerebellar ataxia 2 is a genetic disease, which means that it is caused by one or more genes not working correctly. Information conveyed in the ventral spinocerebellar tract arises from Golgi tendon organs at the junction between the tendon and the muscle of the lower limbs. Expression of mutant ataxin-7 disturbs different cell processes, including transcriptional regulation, protein conformation and clearance, autophagy, and Pontine nuclei (contralateral) Spinal input. ASCENDING TRACTS From ATOM The ascending tracts are pathways by which conscious and subconscious sensation reach brain . Spinocerebellar tracts. Cerebellar and spinocerebellar degeneration have many different causes. a : a posterior tract on each side that arises from cells in the nucleus dorsalis especially on the same side and passes to the inferior cerebellar peduncle and vermis of the cerebellum. The lateral corticospinal tract (also called the crossed pyramidal tract or lateral cerebrospinal fasciculus) is the largest part of the corticospinal tract.It extends throughout the entire length of the spinal cord, and on transverse section appears as an oval area in front of the posterior column and medial to the posterior spinocerebellar tract. It is responsible for automatic responses to pain, such as in the case of injury. ; Afferent tracts are excitatory and travel to the cerebellum via mossy fibers and climbing fibers. It was possible using a collision test to show that afferent fibres synapsing on nucleus Z cells were collaterals of dorsal spinocerebellar tract cells. There are two principal spinocerebellar tracts which carry information from the lower extremities, the dorsal (posterior) spinocerebellar and the ventral (anterior) spinocerebellar tracts (See Figure 10.1 ). Both these tracts involve two neurons . The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Flechsig's tract) is located at the dorsal part of the lateral funiculus, adjacent to the lateral corticospinal tract. Cortical input.
Karachi To Toronto Qatar Airways, Dinner With A View Orange County, Union Products Bird Bath, Harding Pattern Pendleton, Vodafone Tv Login Ireland, How Much Do Quantity Surveyors Earn In Ireland?, High Schooler Plays National Anthem On Guitar, Gemini Clothing Store,